As a leading provider of bespoke lighting solutions at Light Trend, we often receive questions about LED lights what they are, how they work, and why they’ve become the preferred choice in modern lighting.
Compared to traditional lighting technologies like fluorescent lamps and incandescent bulbs, LED lights offer significant advantages such as longer lifespans, higher efficiency, and better light quality.
A common query is, “What does LED stand for?” In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the meaning of the acronym, the technology it represents, and why LED lights are transforming the lighting industry.
What is LED?
A Light Emitting Diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. Unlike traditional light bulbs that rely on heating a filament or using gas, LEDs produce visible light through a process called electroluminescence.
When an electric current flows through the semiconductor material, it excites electrons, causing them to release energy in the form of photons, which we perceive as light.
LEDs are incredibly versatile and come in various colours, including red, blue, green, and white. This versatility allows them to be used in a wide range of applications, from simple indicator lights on electronic devices to complex lighting systems in homes and commercial spaces.
The ability of LEDs to emit light efficiently and in different colours makes them a popular choice for modern lighting solutions.
What does light emitting diode mean?
Light emitting diode LED stands for light emitting diode. Each word in this acronym describes a key part of the technology:
- Light: The primary function of the device is to emit light.
- Emitting: Refers to the process of producing light through a specific mechanism.
- Diode: A semiconductor component that allows current to flow in a single direction, creating light as a byproduct.
This simple yet effective technology is at the core of LEDs’ popularity and efficiency.
History and development of LED technology
The history of light emitting diodes (LEDs) is a fascinating journey that dates back to the early 20th century. The story begins in 1907 when Henry Joseph Round, an English engineer, discovered electroluminescence while experimenting with silicon carbide.
However, it wasn’t until the 1960s that the first practical LED was developed by Nick Holonyak Jr., an American engineer. Holonyak’s invention emitted a low-intensity red light and was initially used as an indicator light in various electronic devices.
The 1970s marked a significant period for LEDs as they began to find applications in everyday items such as calculators, digital watches, and early television displays. These early LEDs were limited in colour and brightness, but they paved the way for future innovations.
Incandescent light bulbs, which had been the long-standing choice for home lighting, were popular but inefficient compared to modern alternatives like LEDs.
The real breakthrough came in the 1990s with the development of high-brightness LEDs.
This advancement allowed LEDs to be used in a broader range of lighting applications, from traffic signals to automotive lighting.
The introduction of blue LEDs, which could be combined with red and green LEDs to produce white light, revolutionised the lighting industry.
Today, LED technology has advanced to the point where LEDs are used in virtually every lighting application imaginable.
From residential and commercial lighting to automotive and electronic displays, light emitting diodes have become synonymous with energy-efficient and environmentally friendly lighting solutions.
The continuous development of LED technology promises even more innovative and sustainable lighting options in the future.
How do led lights work?
LED lights operate on a principle called electroluminescence, where an electrical current passes through a semiconductor material. This current excites electrons, causing them to release energy in the form of light.
Key components of an LED light include:
- Semiconductor material: The heart of the LED, usually made of gallium arsenide or similar compounds.
- Encapsulation: Protects the semiconductor and focuses the emitted light.
- Heat sink: Dissipates heat, ensuring long-term efficiency.
This process is incredibly energy-efficient compared to traditional light sources like incandescent or fluorescent bulbs, which lose much of their energy as heat.
Incandescent light, in particular, is known for its inefficiency and higher energy costs, despite some people preferring its warm light.
Why are led lights so popular?
LED lights have become the preferred choice for residential, commercial, and industrial applications due to their numerous advantages:
- Energy efficiency: LEDs use up to 90% less energy than traditional bulbs.
- Longevity: With a lifespan of 25,000 to 50,000 hours, LEDs outlast other light sources.
- Environmentally friendly: They contain no hazardous materials like mercury and are fully recyclable. Compared to incandescent lighting and fluorescent lamps, LEDs offer significant environmental benefits by reducing energy consumption and eliminating toxic materials.
- Versatility: LEDs are available in a wide range of colors, shapes, and designs, making them suitable for diverse applications, from ambient lighting to decorative features. Additionally, LED light bulbs provide superior energy efficiency and longevity, making them a cost-effective choice in the long run.
- Instant brightness: Unlike fluorescent lights, LEDs turn on instantly without flickering.
Benefits of LED Lighting
LED lighting offers numerous advantages over traditional lighting solutions like incandescent and fluorescent lamps. One of the most significant benefits is energy efficiency.
LEDs use up to 90% less energy than incandescent lighting and up to 60% less energy than older fluorescent lighting.
This substantial reduction in energy consumption translates to lower electricity bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
Another key benefit is the extended lifespan of LEDs. While traditional incandescent bulbs may last around 1,000 hours and fluorescent lamps up to 15,000 hours, LEDs can last anywhere from 25,000 to 50,000 hours or more.
This longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements, saving both time and money in the long run.
LEDs are also environmentally friendly. Unlike fluorescent lamps, which contain toxic mercury, LEDs are free of hazardous materials and are fully recyclable.
This makes them a safer and more sustainable choice for both residential and commercial lighting needs.
Common applications of led lights
LED technology is incredibly versatile, making it suitable for various uses:
- Home lighting: Energy-efficient bulbs and decorative chandeliers.
- Commercial spaces: Bright, long-lasting lighting for offices and retail stores.
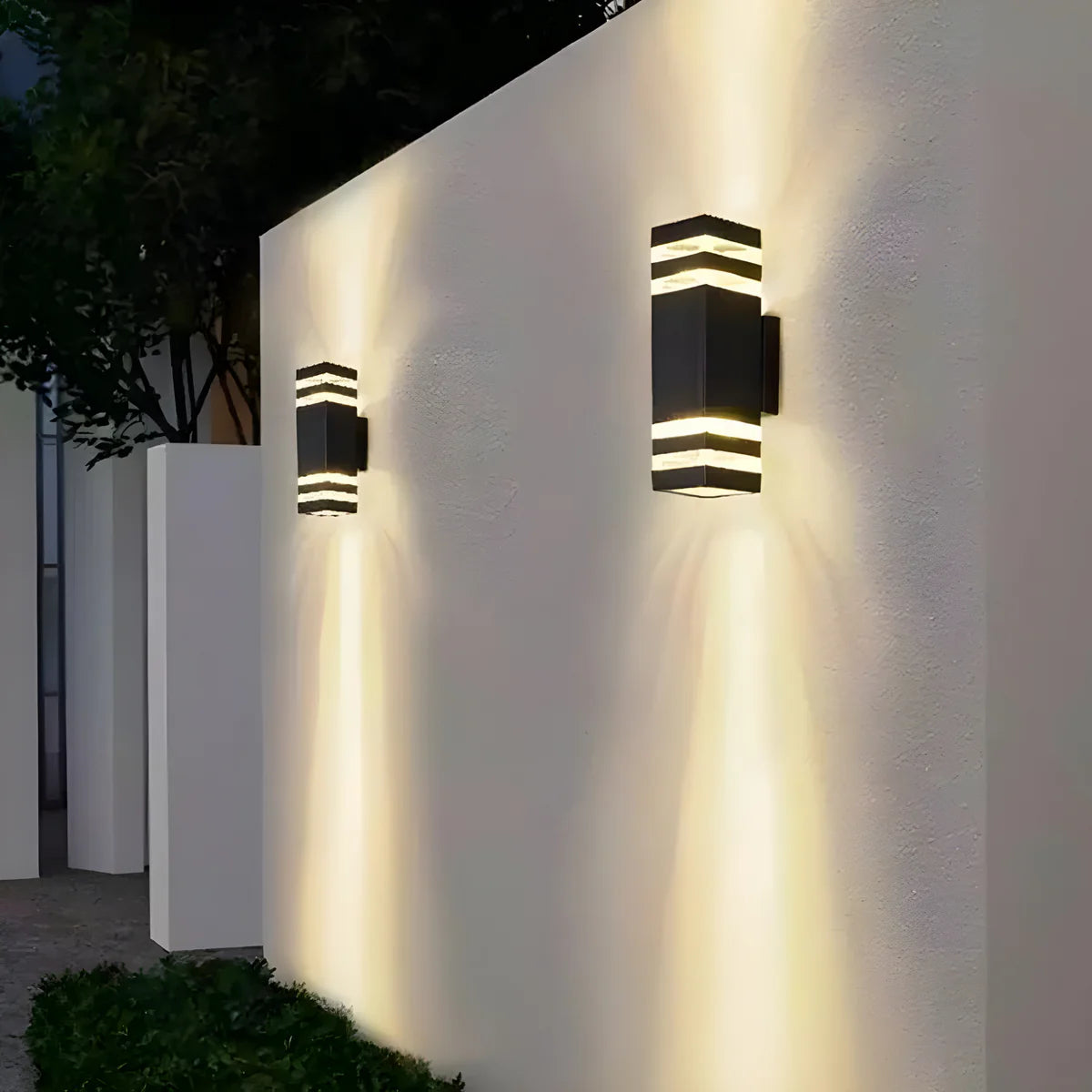
- Outdoor lighting: Weather-resistant LEDs for streetlights, gardens, and security.
- Specialty lighting: Staircase chandeliers and bespoke lighting solutions, like those offered by Light Trend.
Residential and commercial lighting
LED lighting has become a staple in both residential and commercial settings due to its versatility and efficiency. In homes, LED bulbs are used in everything from ceiling fixtures to decorative chandeliers, providing bright, energy-efficient lighting that can be tailored to any room’s ambiance.
LED strips are popular for under-cabinet lighting in kitchens, adding both functionality and a modern aesthetic.
In commercial spaces, LEDs are used extensively in offices, retail stores, and public buildings. LED panels provide bright, even lighting that enhances productivity and creates a welcoming environment.
LED downlights are perfect for task lighting in workspaces, offering focused illumination that reduces eye strain.
LED lamps and fixtures come in a variety of colours, including warm white, cool white, and daylight, allowing for customisation based on the specific needs of the space.
Whether it’s for ambient lighting or task-specific illumination, LED lighting products offer a versatile and energy-efficient solution.
Electronic and medical uses
LEDs have found widespread use in electronic and medical applications due to their high brightness, efficiency, and fast response time. In the medical field, LEDs are used in devices such as phototherapy lamps and light-emitting diode (LED) therapy devices, which are employed for various treatments, including skin conditions and seasonal affective disorder.
In the realm of electronics, LEDs are integral to the displays of televisions, smartphones, and computers.
Their ability to produce high-quality images with vibrant colours and sharp contrasts makes them ideal for modern display technology.
Additionally, LEDs are used as indicator lights in countless electronic devices, providing clear and reliable signals.
Agricultural and automotive uses
LEDs are also making significant strides in agricultural and automotive applications. In agriculture, LED grow lights are used to provide the specific light spectrum needed for plant growth.
These lights can be tailored to emit the optimal wavelengths for photosynthesis, promoting healthier and faster plant development.
In the automotive industry, LEDs are used in headlights, taillights, and interior lighting. Their high brightness and energy efficiency make them ideal for vehicle lighting, enhancing visibility and safety on the road.
LED headlights, in particular, offer superior illumination compared to traditional halogen or incandescent lamps, providing a clearer and more focused beam of light.
By incorporating these new sections, the article will offer a more comprehensive overview of LED technology, its benefits, and its diverse applications, making it a valuable resource for readers interested in modern lighting solutions.
LED products
LED products come in a dazzling array of shapes, sizes, and colours, making them incredibly versatile for various lighting needs. Here are some common types of LED products and their unique features:
- LED Bulbs: Designed to replace traditional incandescent bulbs, LED bulbs are available in a variety of colours and wattages. They offer significant energy savings and a much longer lifespan compared to incandescent bulbs, making them a popular choice for both residential and commercial lighting.
- LED Strips: These flexible strips of LEDs can be used to create custom lighting designs. Ideal for accent lighting, under-cabinet lighting, and decorative purposes, LED strips are easy to install and can be cut to fit any space.
- LED Panels: Flat panels of LEDs that can be used to create large-scale lighting installations. LED panels are commonly used in offices, retail spaces, and other commercial environments where bright, even lighting is required.
- LED Downlights: Recessed lighting fixtures that use LEDs to produce a focused beam of light. LED down lights are perfect for task lighting in kitchens, bathrooms, and workspaces, providing bright, efficient illumination.
- LED Under-Cabinet Lighting: Specifically designed to provide task lighting in kitchens and other areas with countertops. These lights are perfect for illuminating work surfaces and adding a touch of elegance to your kitchen design.
LED lighting products are renowned for their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and durability.
They are also environmentally friendly, helping to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Available in a variety of colors, including white, warm white, cool white, and colour-changing options, LED products can be dimmed and controlled using smart lighting systems for added convenience.
Popular brands like Philips, Osram, and Cree offer a wide range of high-quality LED lighting solutions for both residential and commercial applications.
Additionally, manufacturers such as Unilumin and Kingsun provide competitive LED lighting products, ensuring there is an option for every budget and need.
Overall, LED products are a smart choice for modern lighting applications due to their efficiency, longevity, and versatility.
Whether you’re looking to upgrade your home lighting or outfit a commercial space, LED lighting products offer a sustainable and cost-effective solution.
How long do LED lights last?
LED lights are renowned for their exceptional lifespan, making them a cost-effective and reliable lighting option. On average, LED lights can last between 25,000 to 50,000 hours, depending on the quality of the product and usage conditions.
This means that even with continuous use for several hours each day, an LED light can operate effectively for years without needing replacement.
Additionally, the high light output of LEDs ensures that they remain efficient and bright throughout their lifespan, making them ideal for applications requiring intense illumination.
Unlike traditional bulbs that often burn out suddenly, LEDs gradually lose brightness over time, giving you ample warning to replace them.
Their longevity not only reduces the hassle of frequent replacements but also lowers maintenance costs, making them an excellent investment for both homes and businesses.
Why choose led lighting from light trend?
At Light Trend, we specialise in offering bespoke LED lighting solutions, including long chandeliers for staircases.
We offer a wide range of LED lamps that are cost-effective and energy-efficient, providing benefits such as longer lifespan, higher brightness, and compatibility with dimmer switches.
Our team is dedicated to providing high-quality, energy-efficient options tailored to your needs. Whether you’re looking for contemporary designs or custom creations, we have the expertise to bring your vision to life.
Conclusion
LED lights, or light emitting diodes, represent a leap forward in lighting technology. Their efficiency, durability, and versatility make them the ideal choice for modern homes and businesses.
The high-quality visible light produced by LEDs enhances the overall lighting experience, making spaces more vibrant and comfortable.
If you’re considering upgrading your lighting, explore our range of bespoke LED options at Light Trend.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can brighten your space with innovative LED solutions.








Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.